Overview
Electroplating has long been a widely used technique for applying metal coatings to electronic components, such as electrical interconnects, fasteners, pins and so on. The application of precious and non-precious metals to specific locations on parts enable engineers to improve characteristics such as connectivity, solderability, mechanical protection and anti-corrosion properties.
With many of these types of parts being required to be produced in very high volumes, it is critical that today’s electroplating processes are able to support high production throughput while maintaining consistent quality results. Also, as many electroplating processes use expensive precious metals, precision control over the amounts applied is critical to achieving cost targets for the parts.
This Tech Bulletin provides an overview of advanced reel-to-reel electroplating processes, which provide a combination of selective plating flexibility, tight quality control, and the ability to quickly ramp-up from prototype to sustainable high-volume production.
Electroplating Basics
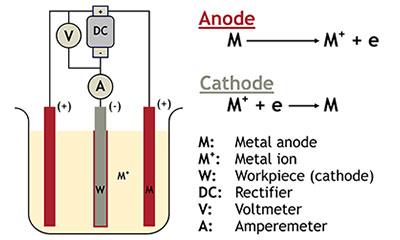
Electroplating is a process by which metal ions migrate via a solution from a positive electrode (anode) to a negative one (cathode). An electrical current passing through the solution causes the workpiece at the cathode to be coated by the metal in the solution.
Electroplating is compatible with a wide range of precious and non-precious metals, including:
- Gold (hardened or soft)
- Palladium
- Indium
- Silver and Silver-Tin
- Copper
- Nickel and Nickel-Phosphorus
- RoHS compliant Tin
Reel-to-Reel Plating Overview
Electroplating may use a variety of approaches, including barrel plating, rack plating and continuous reel-to-reel plating. Parts that have been pre-singulated into separate pieces typically can only be plated via the barrel or rack approaches, which can be time-consuming and/or difficult to control the precision needed for selective plating.

Conversely, continuously-stamped components can be efficiently plated by advanced reel-to-reel methodologies. As pioneered by ENNOVI, the reel-to-reel methodology uniformly presents the continuously-reeled parts to the plating operation in a consistently repeatable manner, which assures greater precision of the results while delivering much higher throughput and yields.
Consistent Positioning Enables Precision Selective Plating
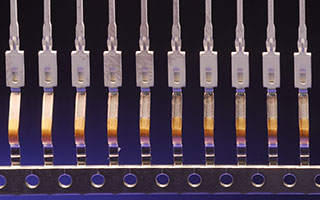
A key advantage of the reel-to-reel approach is the ability to precisely control selective plating options. With all of the continuously reeled parts consistently presented in the same orientation, it is much easier to integrate controlled-depth, spot and stripe plating processes.
Controlled-depth plating provides coverage around the entire circumference of each part with precision depth. Spot plating enables exact targeting of specific areas on each part. Stripe plating allows for highly efficient plating of specific areas across a series of parts in a single pass.
Selective Application of Precious Metals Offers Significant Cost Savings
Since the use of precious metals is one of the key cost factors in many plating applications, the ability to precisely control the amount of material used can be a critical element in achieving cost targets and can provide significant savings in high-volume production scenarios.
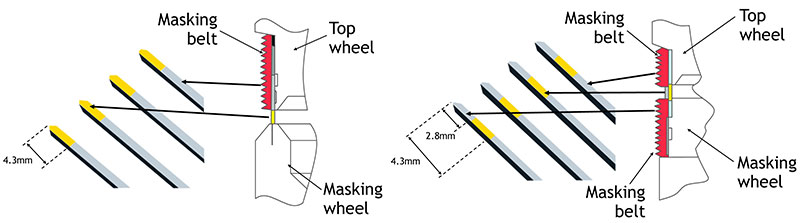
One very useful variation on the selective plating alternatives described above is the use of Front and Rear Side (FRS) plating techniques. As the name implies, this involves only plating two of the four sides on a square pin, which often can achieve the specified electrical conductivity objectives while minimizing the amount of expensive metal being applied. Impressive levels of precious metal savings are attainable with FRS plating, inevitably bringing about valuable cost savings.
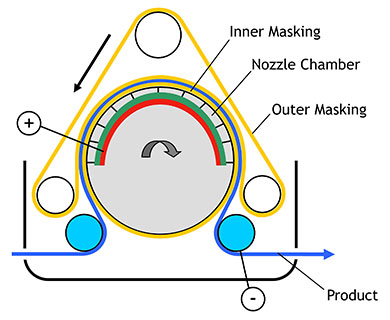
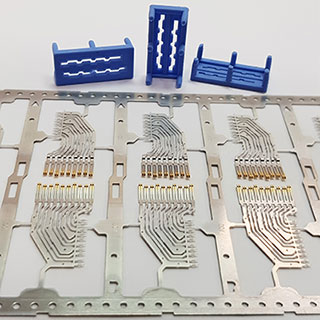
Spot plating offers another approach where significant precious metal savings are possible. Figure 5 illustrates the vertical spot wheel technology, which can be used for Nickel, Silver, Gold, Palladium and Palladium-Nickel plating, just to name a few. Figure 6 shows a spot plated component with the spot wheel insert that defines the selective plating area. Depending on the component and its annual production volume, this technique can be extremely cost effective and also allow for multiple areas of functionality over the component, which can be especially desirable for design engineers.
Summary & Future Opportunities
The ability of advanced reel-to-reel plating processes to tightly control key parameters, such as selective application of plating materials along with sustained high-throughput is delivering unprecedented efficiency and cost savings for applications requiring plating.
In addition, the adaptability of reel-to-reel plating to accommodate a wide range of metals, along with the tight process control parameters have opened doors to effectively address other production issues. For example, ENNOVI is currently experimenting with the use of proprietary IndiCoat™, an Indium whisker-mitigation plating chemistry that can significantly reduce whiskers compared to some Tin plating chemistries.
With the evolution of advanced reel-to-reel techniques, electroplating has entered a whole new phase of application flexibility and precision control that is expanding product design options and production efficiency well beyond the limitations of conventional plating methods.
For More Information
For more information about our plating solutions, drop us an email at communications@ennovi.com.
