Understanding Global Internet Energy Usage & Trends
Data Centers Offer Significant Opportunities for Efficiency Gains
Overview
In this edition of Flash Facts, we take a look at how global Information and Communications Technology (ICT) impacts overall energy usage and to assess some of the things that can be done to help mitigate the impacts of explosive Internet growth.
Quick Overview of Internet Statistics:
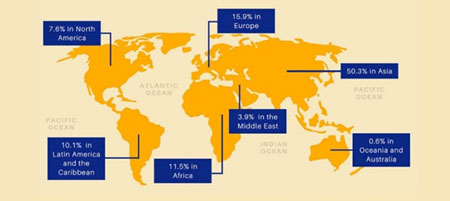
It is impossible today to imagine a world without the internet. As of January 2021, there were 4.66 billion active internet users worldwide, representing 59.5 percent of the global population. Internet usage is spread across all continents, with Asia having over 50 percent of the total users, followed by Europe, Africa, Latin America, and North America.
There are approximately 30 billion internet-connected devices in the world, including computers, smartphones, TVs, tablets, and the fast-growing Internet of Things (IoT) category. IoT currently accounts for more than 10 billion connected devices, such as health trackers, smart-home devices, smart vehicles, and the rapidly rising usage of IoT devices for industrial and supply chain applications. It is estimated that the number of IoT devices alone will surpass 25.4 billion by 2030.
The combination of IoT, 5G wireless, Big Data, AI applications, Industry 4.0 initiatives, rich content streaming, dynamic digital solutions, and subscription-based business models continues to radically transform how companies and consumers use the internet. This further drives the need for ICT solutions to handle more data, higher speeds and wider network expansion.
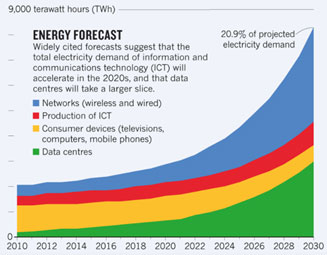
How Much Energy Does the Internet Consume?
Estimates and projections of total internet energy usage vary, with some indicating the internet could use up to 20 percent of all global electricity and emit 5.5 percent of the world’s carbon by 2030.
Data centers account for a significant portion of overall ICT energy usage, which on the surface could seem alarming but there is a silver lining in that data centers also offer key opportunities for mitigating energy usage.
Energy Usage Mitigation Opportunities:
Over the past decade, there has been a major shift from corporate data centers to huge hyperscale cloud data centers that now serve an overwhelming majority of internet traffic. This concentration creates a focus area where changes in energy consumption and electricity sourcing can make big differences.
According to the New York Times, “In 2010, an estimated 79 percent of data center computing was done in traditional computer centers. By 2018, 89 percent of data center computing took place in cloud data centers.” These big cloud providers displaced vastly less efficient corporate data centers, while also shifting the energy usage toward strategies built around sustainability.
An article published recently in the Joule scientific journal, cites the cases of two large international network operators, Telefónica and Cogent, based on reported data traffic and energy use for the COVID year of 2020. Telefónica handled a 45 percent jump in data on its network with no increase in energy use. Cogent’s electricity use fell 21 percent even as data traffic increased 38 percent.
Looking at the shift toward huge hyperscale data centers operated by companies such as Alibaba, Amazon, Apple, Facebook, Google and Microsoft, shows overall energy usage trends that are cause for optimism.
During the period from 2010 to 2018, global data centers saw aggregate workload increases of 2,600 percent, however, total energy consumption only increased by 10 percent overall. This was mainly a result of the huge shift of workloads away from traditional data centers run by non-tech companies into more efficient cloud data centers.
This consolidation has enabled the huge cloud data center providers to initiate strategic programs for lowering their energy consumption and targeting usage of green energy sources. For example, in May 2021, Google announced plans to power all their data centers with renewable energy by 2030. Amazon has also announced plans to power all their Amazon Web Services (AWS) data centers using renewable energy sources by 2025.
With 32 percent share of the cloud markets, AWS can have a huge impact by making efficiency improvements far beyond what each of their separate customers could achieve on their own. Because all the huge cloud services providers have flexibility to locate their hyperscale data centers anywhere, the strategic trend has been to invest in locations with access to abundant renewable sources, such as wind, solar, geothermal or hydroelectric power.
Summary:
While it is important to keep in mind ways to mitigate the significant energy usage from the 30 billion (and growing) number of connected devices that are ultimately driving overall ICT usage, focusing in on the huge opportunities for savings in the data center sector is a big step by itself.
At Interplex, we are proud to be a committed partner and leading innovator in both the Information and Communications Technology sector and the Green Energy sector. We have worked closely with network systems and data center providers to improve performance densities, create more compact systems, improve thermal performance and reduce overall energy usage. On the power generation side of the equation, we are also a key partner to many of the leading renewables players, helping them create innovative high efficiency solar, wind and other green power generation platforms.

For more information about solutions for energy efficient ICT, drop us an email at communications@interplex.com.