BusMate® Pluggable Busbar Connector Technology Enables Advanced Two-Way EV Charging Systems
One of the key e-Mobility applications for the BusMate® Pluggable Busbar Connector system is to streamline the design and assembly of EV charging systems. As discussed in this document, the expanding range of different EV charging scenarios is requiring increasingly complex and sophisticated on-vehicle capabilities, which have raised the bar for technology solutions such as BusMate® that can provide robust power interconnects between PCBs and to external power sources.
Trends in EV Charging
The ongoing build-out of EV charging infrastructure is a critical factor for widespread consumer adoption of electric vehicles.
DC Fast charging has become the preferred method because of its ability to charge EVs much faster than regular AC charging. DC can typically charge an EV to 80 percent in between 15-30 minutes, which makes usage of EVs for longer trips more practical.
DC Fast charging has become the preferred method because of its ability to charge EVs much faster than regular AC charging. DC can typically charge an EV to 80 percent in between 15-30 minutes, which makes usage of EVs for longer trips more practical.

Two-way charging is also becoming an expected feature for most new EVs in order to support these types of scenarios:
- Vehicle to Grid (V2G) – enables EVs to send power upstream back into the grid, which holds the potential for improving overall electrical usage and sustainability and offset peaks in demand by tapping into EVs charging at home stations. Essentially, this turns thousands of EVs into connected battery storage for electrical grids.
- Vehicle to Home (V2H) – enables individuals to use their EVs as privately connected power sources that improve their personal energy consumption patterns. For instance, an EV could be charged at night when there is less demand on the grid and costs are lower and, then the EV could provide power to the home during the day when costs are higher.
Advanced On-board Chargers Require New Technology Approaches
To achieve the advanced, two-way, Smart Charging capabilities described above, new-generation on-vehicle charging systems are undergoing transformational changes. Increasingly, EV on-board charger designs entail multi-functional, multi-PCB configurations with built-in intelligence to manage the DC-to-DC charging processes.
This increased complexity is part of the overall power trends in EV mobility applications, in which current levels and functional integration are increasing as shown below:
This increased complexity is part of the overall power trends in EV mobility applications, in which current levels and functional integration are increasing as shown below:
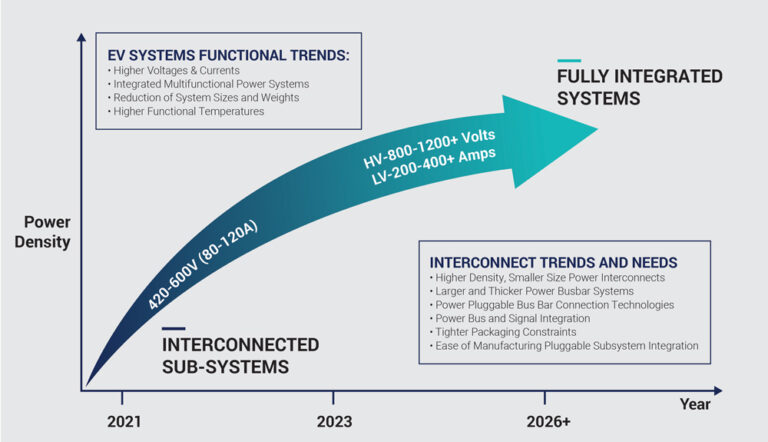
Figure 1 – EV Mobility Power Trends
Power interconnects have become a critical factor for connecting multiple PCBs such as control boards and power modules in the charger assembly, while keeping overall size, cost, and assembly steps to a minimum. Key factors for success include:
- High ampacity-to-size ratios
- Robust contact interfaces
- Consistent coupling with auto-compensation for tolerance variations
- Small footprints to minimize PCB real estate usage
- PCB attachment options for through-hole, SMT and Press-Fit

Figure 2 – BusMate®‘s Small Footprint
Interplex’s BusMate® Power Interconnect System Addresses All These Key Factors
BusMate® combines a small footprint to conserve PCB space with a large ampacity-to-size ratio for handling increasing power densities.
To accommodate a range of applications, BusMate® power couplers are available in SMT format or proven eye-of-the-needle solderless Press-Fit interfaces.
To accommodate a range of applications, BusMate® power couplers are available in SMT format or proven eye-of-the-needle solderless Press-Fit interfaces.
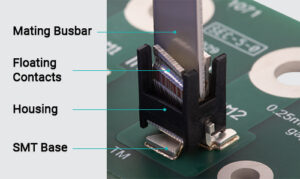
Figure 3 – BusMate® Connector
Robust Electrical Performance, Ease of Assembly and Configuration Flexibility
BusMate® ensures low and stable contact resistance while allowing for wide positional tolerance of the mating blade in all three axes. Interplex’s Floating Contact Technology assures consistent high-power coupling by automatically compensating for variations in blade alignment.
BusMate®’s pluggable Floating Contact Technology can accommodate large assembly tolerances of +/- 0.8mm offset and up to +/- 16 degrees of twist. In addition, it can handle a range of insertion depths and accommodate up to three re-mating cycles with no loss of performance.
BusMate®’s pluggable Floating Contact Technology can accommodate large assembly tolerances of +/- 0.8mm offset and up to +/- 16 degrees of twist. In addition, it can handle a range of insertion depths and accommodate up to three re-mating cycles with no loss of performance.
Improved Design and Production for Power Interconnects
BusMate® is well suited to address the application-specific requirements for a wide range of advanced on-board charger designs. As shown in Figure 3, BusMate® can be used for a variety of interconnect scenarios including AC, DC, PCB-to-PCB, fuses, transformers, etc.
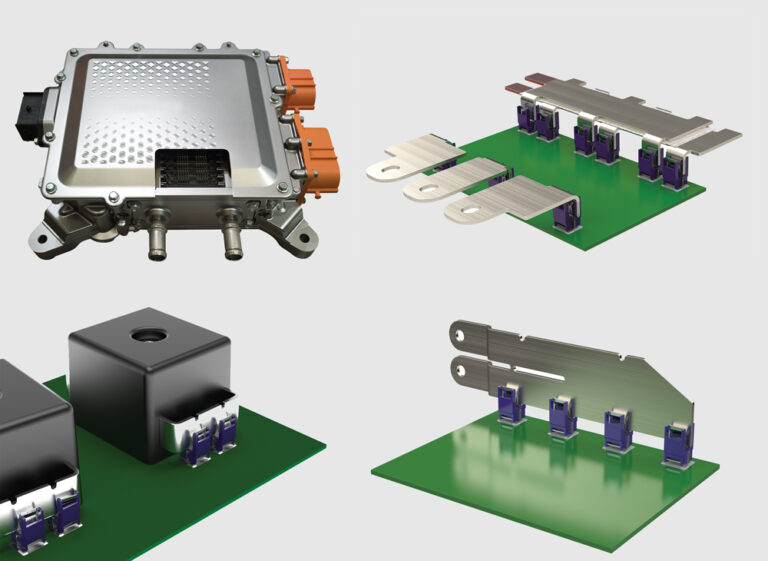
Figure 4 – BusMate® Power Applications
Of particular importance in on-board EV chargers, is the use of BusMate® for small-footprint, robust PCB-to-PCB interfaces. As shown in Figure 4, multiple BusMate® terminals can provide compact, power interfaces between boards.
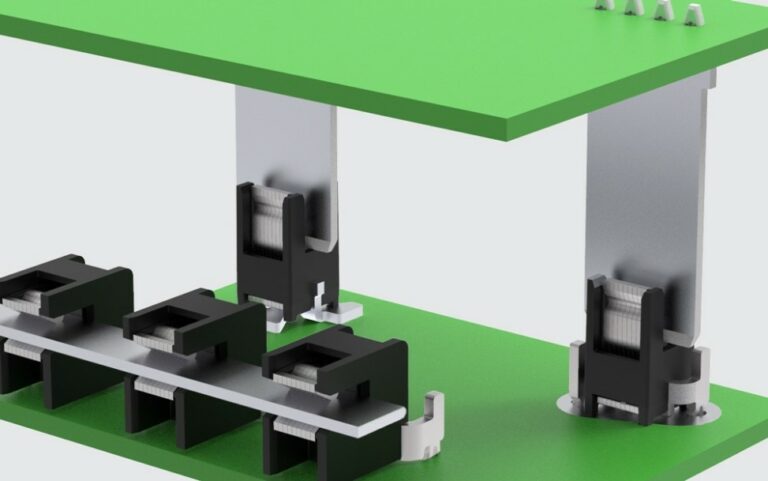
Figure 5 – BusMate® PCB-to-PCB Interconnects
BusMate®’s Floating Contact System provides ample positional tolerance to support large variations in mating blade offsets to enhance blind mating scenarios for ease of assembly, which both lowers costs and provides high volume production efficiency and reliability.
Summary
As two-way charging and Smart Charging applications make on-board EV systems more complex and overall power densities increase, the need to integrate a variety of functions and minimize size while improving power efficiency will be critical for sustainable e-Mobility success.
A high degree of configuration flexibility, combined with compact size, high power density and cost-effective volume manufacturing make BusMate® a logical choice for use across the widening range of power connectivity requirements in both current and emerging application areas.
A high degree of configuration flexibility, combined with compact size, high power density and cost-effective volume manufacturing make BusMate® a logical choice for use across the widening range of power connectivity requirements in both current and emerging application areas.




